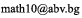Transformation of Coordinates Involving Pure Translation

where (x, y) are old coordinates [i.e. coordinates relative to xy system], (x',y') are new coordinates [relative to x'y' system] and (x0, y0) are the coordinates of the new origin 0' relative to the old xy coordinate system.
Transformation of Coordinates Involving Rotation

$\begin{cases}x = x' \cos\alpha - y' \sin\alpha \\ y = x' \sin\alpha + y' \cos\alpha \end{cases}$
or
$\begin{cases}x' = x \cos\alpha + y \sin\alpha \\ y' = y \cos\alpha - x \sin\alpha \end{cases}$
where the origins of the old [xy] and new [x'y'] coordinate systems are the same but the x' axis makes an angle α with the positive x axis.
Transformation of Coordinates Involving Translation and Rotation

or
$x' = (x - x_0)\cos\alpha + (y - y_0)\sin\alpha \\ y' = (y - y_0)\cos\alpha - (x - x_0)\sin\alpha$where the new origin O' of x'y' coordinate system has coordinates (x0, y0) relative to the old xy coordinate system and the x' axis makes an angle α with the positive x axis.
Polar Coordinates(r, θ)
A point P can be located by rectangular coordinates (x, y) or polar coordinates (r, θ). The transformation between these coordinates


 MENU
MENU