Hyperbolic Functions - sinh, cosh, tanh, coth, sech, csch
Definition of hyperbolic functions
Hyperbolic sine of x
$\text{sinh}\ x = \frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{2}$
Hyperbolic cosine of x
$\text{cosh}\ x = \frac{e^x + e^{-x}}{2}$
Hyperbolic tangent of x
$\text{tanh}\ x = \frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}}$
Hyperbolic cotangent of x
$\text{coth}\ x = \frac{e^x + e^{-x}}{e^x - e^{-x}}$
Hyperbolic secant of x
$\text{sech}\ x = \frac{2}{e^x + e^{-x}}$
Hyperbolic cosecant of x
$\text{csch}\ x = \frac{2}{e^x - e^{-x}}$
Relationship among hyperbolic functions
$\text{tanh}\ x = \frac{\text{sinh}\ x}{\text{cosh}\ x}$
$\text{coth}\ x = \frac{1}{\text{tanh}\ x} = \frac{\text{cosh}\ x}{\text{sinh}\ x}$
$\text{sech}\ x = \frac{1}{\text{cosh}\ x}$
$\text{csch}\ x = \frac{1}{\text{sinh}\ x}$
$\text{cosh}^2x - \text{sinh}^2x = 1$
$\text{sech}^2x + \text{tanh}^2x = 1$
$\text{coth}^2x - \text{csch}^2x = 1$
Functions of negative arguments
sinh(-x) = -sinh x
cosh(-x) = cosh x
tanh(-x) = -tanh x
csch(-x) = -csch x
sech(-x) = sech x
coth(-x) = -coth x
Addition fomulas
$\text{sinh}(x \pm y) = \text{sinh}\ x \ \text{cosh}\ y \pm \text{cosh}\ x\ \text{sinh}\ y$
$\text{cosh}(x \pm y) = \text{cosh}\ x\ \text{cosh}\ y \pm \text{sinh}\ x\ \text{sinh}\ y$
$\text{tanh}(x \pm y) = \frac{\text{tanh}\ x \pm \text{tanh}\ y}{1 \pm \text{tanh}\ x \cdot \text{tanh}\ y}$
$\text{coth}(x \pm y) = \frac{\text{coth x}\ \text{coth}\ y \pm l}{\text{coth}\ y \pm \text{coth}\ x}$
Double angle formulas
$\text{sinh}\ 2x = 2 \text{sinh}\ x\ \text{cosh}\ x$
$\text{cosh}\ 2x = \text{cosh}^2x + \text{sinh}^2x= 2 \text{cosh}^2x - 1 = 1 + 2 \text{sinh}^2x$
$\text{tanh}\ 2x = \frac{2\text{tanh}\ x}{1 + \text{tanh}^2x}$
Half angle formulas
$\sinh \frac{x}{2} = \pm \sqrt{\frac{\cosh x - 1}{2}}$ [+ if x > 0, - if x < 0]
$\cosh \frac{x}{2} = \sqrt{\frac{\cosh x + 1}{2}}$
$\tanh \frac{x}{2} = \pm \sqrt{\frac{\cosh x - 1}{\cosh x + 1}}$ [+ if x > 0, - if x < 0]
$=\frac{\text{sinh}(x)}{1 + \text{cosh}(x)} = \frac{\text{cosh}(x) - 1}{\text{sinh}(x)}$
Multiple angle formulas
$\sinh 3x = 3 \sinh x + 4 \sinh^3 x$
$\cosh 3x = 4 \cosh^3 x - 3 \cosh x$
$\tanh 3x = \frac{3 \tanh x + \tanh^3 x}{1 + 3 \tanh^2x}$
$\sinh 4x = 8 \sinh^3 x\ \cosh x + 4 \sinh x\ \cosh x$
$\cosh 4x = 8 \cosh^4 x - 8 \cosh^2 x + 1$
$\tanh 4x = \frac{4 \tanh x + 4 \tanh^3 x}{1 + 6 \tanh^2 x + \tanh^4 x}$
Powers of hyperbolic functions
$\text{sinh}^2 x = \frac12 \text{cosh}\ 2x - \frac12$
$\text{cosh}^2 x = \frac12 \text{cosh}\ 2x + \frac12$
$\text{sinh}^3 x = \frac14 \text{sinh}\ 3x - \frac34 \text{sinh}\ x$
$\text{cosh}^3 x = \frac14 \text{cosh}\ 3x + \frac34 \text{cosh}\ x$
$\text{sinh}^4 x = \frac{3}{8} - \frac12 \text{cosh}\ 2x + \frac18 \text{cosh}\ 4x$
$\text{cosh}^4 x = \frac{3}{8} + \frac12 \text{cosh}\ 2x + \frac18 \text{cosh}\ 4x$
Sum, difference and product
$\text{sinh}\ x + \text{sinh}\ y = 2 \text{sinh}\ \frac12(x + y)\ \text{cosh}\ \frac12(x - y)$
$\text{sinh}\ x - \text{sinh}\ y = 2 \text{cosh}\ \frac12(x + y)\ \text{sinh} \frac12(x - y)$
$\text{cosh}\ x + \text{cosh}\ y = 2 \text{cosh}\ \frac12(x + y)\ \text{cosh}\ \frac12(x - y)$
$\text{cosh}\ x - \text{cosh}\ y = 2 \text{sinh}\ \frac12(x + y)\ \text{sinh}\ \frac12(x - y)$
$\text{sinh}\ x\ \text{sinh}\ y = \frac12(\text{cosh}(x + y) - \text{cosh} (x - y))$
$\text{cosh}\ x\ \text{cosh}\ y = \frac12(\text{cosh}(x + y) + \text{cosh} (x - y))$
$\text{sinh}\ x\ \text{cosh}\ y = \frac12(\text{sinh}(x + y) + \text{sinh} (x - y))$
Expression of hyperbolic functions in terms of others
In the following we assume x > 0. If x < 0 use the appropriate sign as indicated by formulas in the section "Functions of Negative Arguments"
Graphs of hyperbolic functions
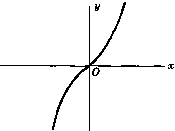

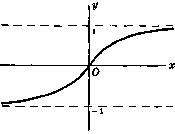
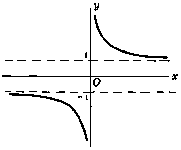
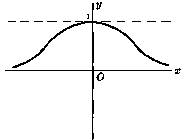
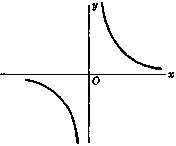
Inverse hyperbolic functions
If x = sinh y, then y = sinh-1 a is called the inverse hyperbolic sine of x. Similarly we define the other inverse hyperbolic functions. The inverse hyperbolic functions are multiple-valued and as in the case of inverse trigonometric functions we restrict ourselves to principal values for which they can be considered as single-valued.
The following list shows the principal values [unless otherwise indicated] of the inverse hyperbolic functions expressed in terms of logarithmic functions which are taken as real valued.
$\sinh^{-1} x = \ln(x + \sqrt{x^2 + 1})$ $-\infty < x < \infty$
$\cosh^{-1} x = \ln(x + \sqrt{x^2 - 1})$ $x \geq l$ [$\cosh^{-1} x > 0$ is principal value]
$\tanh^{-1} x = \frac{1}{2} \ln\frac{(1 + x)}{(1 - x)}$ $- 1 < x < 1$
$\coth^{-1} x = \frac{1}{2} \ln\frac{(x + 1)}{(x - 1)}$ $x > 1$ or $x < -1$
$\text{sech}^{-1} x = \ln(\frac{1}{x} + \sqrt{\frac{1}{x^2} - 1})$ $0 < x \leq l$ [$\text{sech}^{-1} x > 0$ is principal value]
$\text{csch}^{-1} x = \ln(\frac{1}{x} + \sqrt{\frac{1}{x^2} + 1})$ $x \neq 0$
Relationship between inverse hyperbolic functions
csch-1 x = sinh-1 (1/x)
sech-1 x = cosh-1 (1/x)
coth-1 x = tanh-1 (1/x)
sinh-1(-x) = -sinh-1x
tanh-1(-x )= -tanh-1x
coth-1 (-x) = -coth-1x
csch-1 (-x) = -csch-1x
Graphs of inverse hyperbolic functions
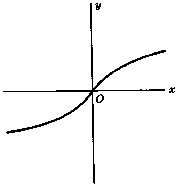

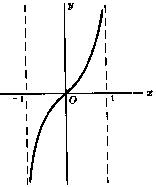
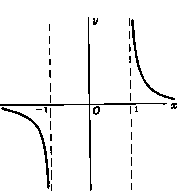
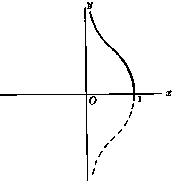

Relationship between hyperbolic and trigonometric functions
Periodicity of hyperbolic functions
In the following $k$ is any integer.
$\text{sinh} (x + 2k \pi i) = \text{sinh}\ x$ $\text{csch} (x + 2k\pi i) = \text{csch} x$
$\text{cosh} (x + 2k \pi i) = \text{cosh}\ x$ $\text{sech} (x + 2k\pi i) = \text{sech} x$
$\text{tanh} (x + k\pi i) = \text{tanh}\ x$ $\text{coth} (x + k\pi i) =\text{coth} x$

 MENU
MENU